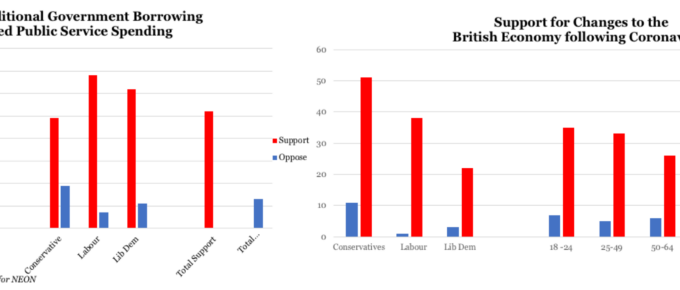
While it is still uncertain how the United Kingdom’s economic policy will be reframed by the pandemic, Boris Johnson and Rishi Sunak have already publicised what they term a ‘Rooseveltian’ approach to the economy, striving to strengthen public spending across multiple sectors of the economy.
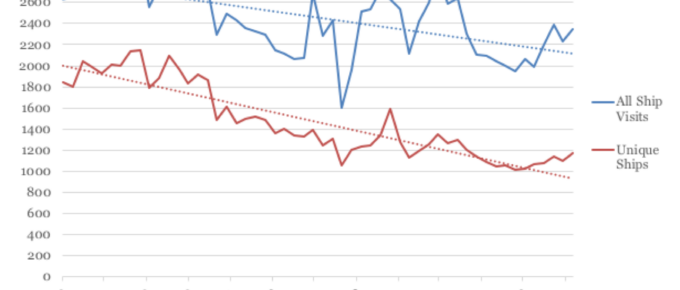
The Impact of COVID 19 on Shipping
Concerns exist around the possibility of new barriers and local regulations in global maritime trade, or that nations seek to extend their flag protected fleets, leading some to expect a particularly painful and stilted recovery.
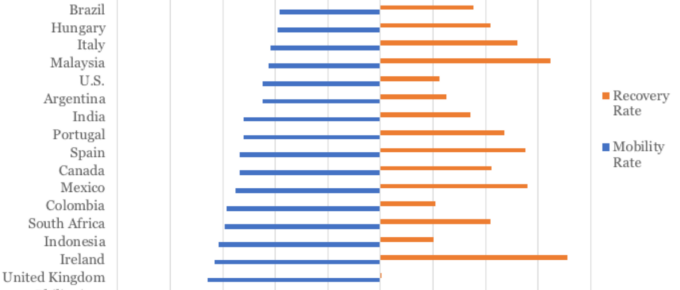
Nations Re-Opening after Covid 19
As the world emerges from the pandemic questions arise about how the global economy will be augmented or reshaped by the events of 2020. After the 2008 crash, Brexit and the US-China trade war, the incoming Chief Economist of the World Bank, Carmen Reinhart, describes the pandemic as the ‘last nail in the coffin of globalisation’. So as much..
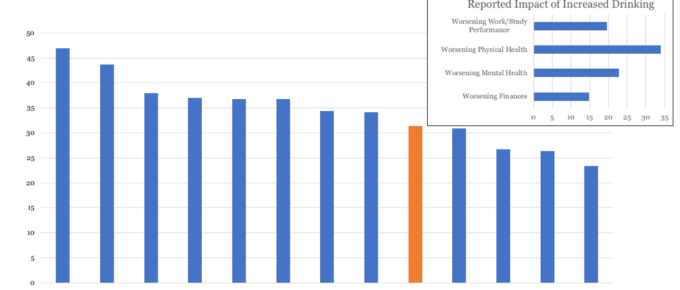
Covid 19, Alcohol Use and Mental Health
Pre-pandemic research found heightened risk from working under certain conditions such as in isolation away from friends and family; extended or shift-pattern working hours, in dangerous environments, under inadequate supervision or at risk from organisational change (restructure/redundancy)- a list that makes clear what may be driving this Covid related increase in consumption.
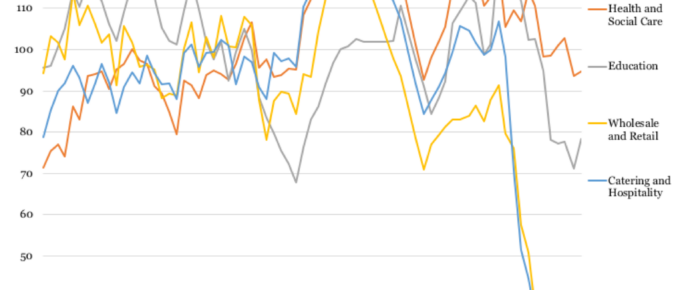
Covid 19: Effect on Job Vacancies by Sector
Those in lower-earning jobs offering £15-£25 thousand per annum (less than London Living Wage) are worst affected. Higher paid jobs’ greater likeliness to be conducted from home is partly reflected in the far lower reduction in available positions.
COVID 19: Jobs vs Exposure
Looking at pay, over a third of the highest-risk jobs have a below median hourly pay rate (currently £13.21 in the UK). Care escorts, dental nurses, and nursing auxiliaries and assistants are among the lowest paid and all range between £9.45 and £10.93.